Sea ice drift
Sea ice drift on regional scale from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
Sea ice motion can be estimated from a set of two radar images recorded at different points in time. In this project, we have focused on using a pattern-tracking approach to determine the displacement of structures in the sea ice. Figure 3.3 (left) shows an example of ice drift calculated from a pair of spatially overlapping SAR images from 16 September 2012. A technique called back matching is used to identify areas where the ice drift retrieval algorithm yields consistent results. Regions without consistent ice drift vectors are not mapped. The estimate ice motion vectors can be used to derive ice divergence and convergence fields (Figure 1 (right)).
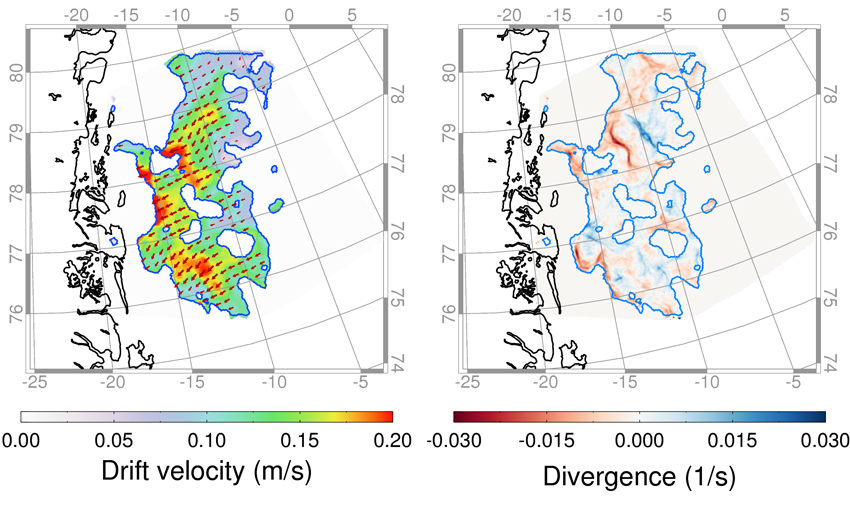
Figure 1:
Examples of an ice drift product calculated from a pair of spatially overlapping SAR images from 16 September 2012. Left: a drift field in the Fram Strait calculated from a pair of Radarsat-2 images, where the velocity magnitude is shown in colours. Right: Calculated ice motion vectors can be used to derive ice divergence and convergence fields.
©AWI
